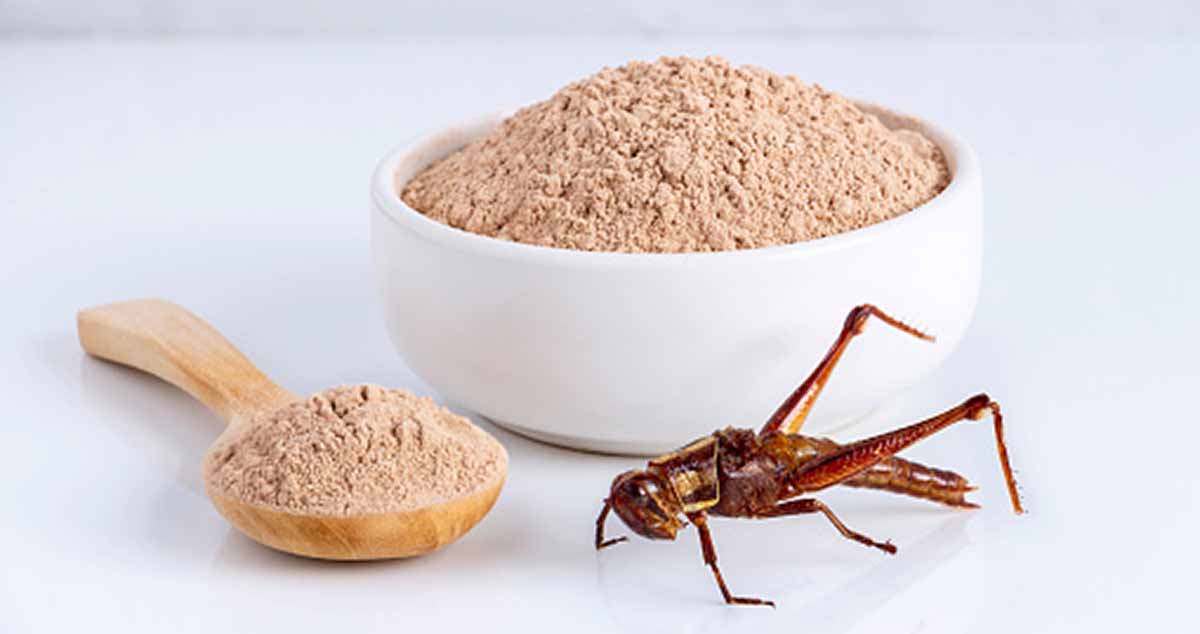
You’ve probably read about the latest in food trends: insects. They’re easy to raise, packed with protein, and can be ground into flour and other ingredients used by restaurants and in packaged foods.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recently announced that mealworms are safe for human consumption, sparking a race to supply cheap, functional insect-derived ingredients to manufacturers clamoring for new options. Don’t expect the US to be far behind.
The fact is you are probably already eating ingredients derived from insects. Shellac, used for crunchy candy coatings and confectioners glaze, is made of a secretion from the female lac bug commonly found in India and Southeast Asia. And Carmine, the red dye used in everything from baked goods to drinks, is derived from the cochineal, a cactus parasite that is dried and ground into a powder.
Now, with a proliferation of novel insect-derived ingredients on the horizon, a new study shows that some bug-based ingredients could be problematic for individuals coping with shellfish allergies. Here follows a press release from Edith Cowan University describing a study identifying 20 proteins found in cricket products alone that could potentially cause serious allergic reactions.
Putting bugs on the menu, safely
NEWS RELEASE 27-JAN-2021 – Edith Cowen University
The thought of eating insects is stomach turning for many, but new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research is shedding light on allergy causing proteins which could pose serious health risks for those suffering from shellfish allergy
The thought of eating insects is stomach turning for many, but new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research is shedding light on allergy causing proteins which could pose serious health risks for those suffering from shellfish allergy.
The research, published in the journal Food Chemistry, identified 20 proteins found in cricket food products which could cause serious allergic reactions.
The project was led by Professor Michelle Colgrave from ECU’s School of Science and the CSIRO.
Professor Colgrave said crickets and other insects could be the key to feeding for the estimated 9.7 billion people on Earth in 2050.
“More than 2 billion people around the world already eat insects on a daily basis and they could be a sustainable solution, providing protein that complements traditional animal-based protein sources,” she said.
“Crickets are high in protein, nutrient dense and considered environmentally friendly.
“Numerous studies have shown eating insects provide benefits to gut health, lowering blood pressure while being high in antioxidants.”
Insects might have a strong reaction
While insects show promise as an alternative protein source, and are identified by Agrifutures as a high potential emerging industry, their allergenic properties are a concern.
As the world searches for novel and more sustainable forms of food, consideration must also be paid to those with allergenic properties and that is where Professor Colgrave’s research fits in.
“This research showed a significant overlap in allergenic proteins found in cricket food products and those found in shellfish like crabs and prawns,” she said.
“That’s because crickets, mealworms and other insects are closely related to crustaceans.
“Shellfish allergies affect up to two per cent of people globally, but varies according to age and region, and there’s a good chance that people allergic to shellfish will also react to insects.”
Being an allergen does not prevent insects being used as a food source, however it does mean that insect-based foods need to be tested and labelled correctly to ensure people with allergies don’t unwittingly eat them.
Breaking down the bugs
The research team from ECU, CSIRO, James Cook University and Singapore’s National Agency for Science Technology and Research compared proteins from roasted whole crickets and cricket powder products to known allergens.
Their results can now be used to detect cricket-derived allergens in food products that can support allergen labelling and safe food manufacture.
###
‘Protein extraction protocols for optimal proteome measurement and arginine kinase quantitation from cricket Acheta domesticus for food safety assessment’ was published in Food Chemistry and can be accessed at the Journal’s webpage.
- 10 natural ingredients you have no idea you’re eating: Fish bladders, bug secretions and more — Los Angeles Times
- Insect Market To Explode: EU Gives Green Light To Eating Mealworm — Forbes
- Edible insects: the science of novel food evaluations — EFSA
- Putting bugs on the menu, safely — Edith Cowen University Press Release