This flu season is already shaping up to be a severe one with cases already reported in 12 states. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend everyone 6 months of age and older get a flu vaccine.
As happens this time of year, we at SnackSafely.com are receiving many inquiries regarding the safety of influenza vaccine for people with food allergies.
First, it should be noted that adverse reactions are extremely rare. A recent CDC study found the rate of anaphylaxis after all vaccines is 1.31 per one million vaccine doses given.
Who shouldn’t get the flu vaccine? The CDC says those that have experienced life-threatening allergies to flu vaccine or any ingredient in the vaccine, which might include include gelatin, antibiotics, or other ingredients. If you suspect you fall in this category, contact your medical professional to determine your eligibility to receive the vaccine.
But what about people with egg allergy… aren’t they supposed to avoid the flu vaccine? In most cases, they should also receive the flu vaccine. To clarify, the CDC issued specific recommendations for people with egg allergy in September, 2016, which are still applicable for the current flu season. Please read the recommendations below in their entirety and contact your medical professional if you have any questions regarding your suitability for the vaccine.
CDC Recommendations Regarding Flu Vaccine for People with Egg Allergy
Summary:
CDC and its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices have updated their guidelines on egg allergy and receipt of influenza (flu) vaccines. Based on the new recommendations, people with egg allergies no longer need to be observed for an allergic reaction for 30 minutes after receiving a flu vaccine. Should it be required, people with a history of severe allergic reaction to egg (i.e., any symptom other than hives) can now be vaccinated in an inpatient or outpatient medical setting (including but not necessarily limited to hospitals, clinics, health departments, and physician offices), under the supervision of any health care provider who is able to recognize and manage severe allergic conditions. Previously, it was recommended that such people be given a flu vaccine only by a doctor with experience in managing severe allergic conditions and that they be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination.
Most flu shots and the nasal spray flu vaccine are manufactured using egg-based technology. Because of this, they contain a small amount of egg proteins, such as ovalbumin. However, studies that have examined the use of both the nasal spray vaccine and flu shots in egg-allergic and non-egg-allergic patients indicate that severe allergic reactions in people with egg allergies are unlikely. A recent CDC study found the rate of anaphylaxis after all vaccines is 1.31 per one million vaccine doses given.
Changes:
Recommendations for flu vaccination of persons with egg allergy have been modified for the 2016-2017 season. CDC recommends:
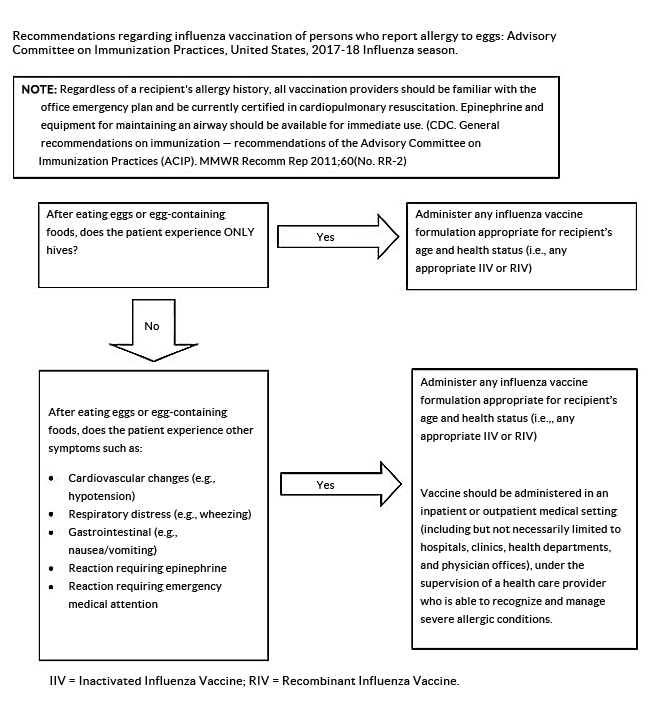
- Persons with a history of egg allergy who have experienced only hives after exposure to egg should receive flu vaccine. Any licensed and recommended flu vaccine (i.e., any form of IIV or RIV) that is otherwise appropriate for the recipient’s age and health status may be used.
- Persons who report having had reactions to egg involving symptoms other than hives, such as angioedema, respiratory distress, lightheadedness, or recurrent emesis; or who required epinephrine or another emergency medical intervention, may similarly receive any licensed and recommended flu vaccine (i.e., any form of IIV or RIV) that is otherwise appropriate for the recipient’s age and health status. The selected vaccine should be administered in an inpatient or outpatient medical setting (including, but not necessarily limited to hospitals, clinics, health departments, and physician offices). Vaccine administration should be supervised by a health care provider who is able to recognize and manage severe allergic conditions.
- A previous severe allergic reaction to flu vaccine, regardless of the component suspected of being responsible for the reaction, is a contraindication to future receipt of the vaccine.
Questions & Answers:
What is considered an egg allergy? What are the signs and symptoms of an egg allergic reaction?
Egg allergy can be confirmed by a consistent medical history of adverse reactions to eggs and egg-containing foods, plus skin and/or blood testing for immunoglobulin E antibodies to egg proteins. Persons who are able to eat lightly cooked egg (e.g., scrambled egg) without reaction are unlikely to be allergic. Egg-allergic persons might tolerate egg in baked products (e.g., bread or cake). Therefore, tolerance to egg-containing foods does not exclude the possibility of egg allergy. Egg allergies can range in severity.
How common is egg allergy in children and adults?
Egg allergy affects about 1.3 % of all children and 0.2 % of all adults.
What vaccine should I get if I am egg allergic, but I can eat lightly cooked eggs?
If you are able to eat lightly cooked egg (e.g., scrambled egg) without reaction, you are unlikely to be allergic and can get any licensed flu vaccine (i.e., any form of IIV, LAIV, or RIV) that is otherwise appropriate for your age and health status.
What flu vaccine should I get if I get hives after eating egg-containing foods?
If you are someone with a history of egg allergy, who has experienced only hives after exposure to egg, you can get any licensed flu vaccine (i.e., any form of IIV, LAIV, or RIV) that is otherwise appropriate for your age and health.
What kind of flu vaccine should I get if I have more serious reactions to eating eggs or egg-containing foods like cardiovascular changes or a reaction requiring epinephrine?
If you are someone who has more serious reactions to eating eggs or egg-containing foods, like angioedema, respiratory distress, lightheadedness, or recurrent emesis; or who required epinephrine or another emergency medical intervention, you can get any licensed flu vaccine (i.e., any form of IIV, LAIV, or RIV) that is otherwise appropriate for your age and health status, but the vaccine should be given by a health care provider who can recognize and respond to a severe allergic response.
Are there still people with egg allergies who should not get flu vaccine?
People with egg allergy can receive flu vaccines according to the recommendations above. A person who has previously experienced a severe allergic reaction to flu vaccine, regardless of the component suspected of being responsible for the reaction should not get a flu vaccine again.
Why do flu vaccines contain egg protein?
Most flu vaccines today are produced using an egg-based manufacturing process and thus contain a small amount of egg protein called ovalbumin.
How much egg protein is in flu vaccine?
While not all manufacturers disclose the amount of ovalbumin in their vaccines, those that did from 2011–12 through 2014–15 reported maximum amounts of ≤1 µg/0.5 mL dose for flu shots and 0.24 µg/0.2 mL dose for the nasal spray vaccine. Cell-based flu vaccine (Flucelvax) likely has a much smaller amount of egg protein since the original vaccine virus is grown in eggs, but mass production of that vaccine does not occur in eggs. Recombinant vaccine (Flublok) is the only vaccine currently available that is completely egg free.
Can egg protein in flu vaccine cause allergic reactions in persons with a history of egg allergy?
Yes, allergic reactions can happen, but they occur very rarely with the flu vaccines available in the United States today. Occasional cases of anaphylaxis, a severe life-threatening reaction that involves multiple organ systems and can progress rapidly, in egg-allergic persons have been reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) after administration of flu vaccine. Flu vaccines contain various components that may cause allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. In a Vaccine Safety Datalink study, there were 10 cases of anaphylaxis after more than 7.4 million doses of inactivated flu vaccine, trivalent (IIV3) given without other vaccines, (rate of 1.35 per one million doses). Most of these cases of anaphylaxis were not related to the egg protein present in the vaccine. CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices continue to review available data regarding anaphylaxis cases following flu vaccines.
How long after flu vaccination does a reaction occur in persons with a history of egg allergy?
Allergic reactions can begin very soon after vaccination. However, the onset of symptoms is sometimes delayed. In a Vaccine Safety Datalink study of more than 25.1 million doses of vaccines of various types given to children and adults over 3 years, only 33 people had anaphylaxis. Of patients with a documented time to onset of symptoms, eight cases had onset within 30 minutes of vaccination, while in another 21 cases, symptoms were delayed more than 30 minutes following vaccination, including one case with symptom onset on the following day.
What happened to the algorithm for recommendations regarding flu vaccination of persons who report allergy to eggs that appeared in last year’s flu vaccine recommendations?
In 2016, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided to remove algorithm for ACIP recommendations regarding flu vaccination of persons who report allergy to eggs from the 2016-2017 guidance. CDC has created an updated version of the algorithm below to reflect the new recommendations.